Accessing the clusters using Secure Shell (SSH)
A remote shell is the most common way of accessing a High-Performance Computing (HPC) cluster. A remote shell allows you to execute commands on another machine as you do sitting in front of it. A remote shell is convenient because it also allows many other machine users to do the same, so you get access to a resource being utilized by tens or hundreds of users simultaneously.
All you need on your computer is a terminal emulator and an SSH client. A terminal emulator is a program that mimics the behavior of old dumb terminals from decades ago. An SSH client is a program on your computer that allows you to connect to another computer using an encrypted channel. In the old times (the 80s), people used to create a remote shell using an unencrypted channel known as Telnet. Today, SSH provides a secure channel over an unsecured network such as the Internet. SSH offers similar capabilities to Telnet but adds encryption, so all data sent and received between your computer and the remote host is encoded in such a way that only your computer and the remote computer can see the data. If you want to learn more about Secure Shell, you can find it on Wikipedia. Currently (2024), WVU offers access to three HPC clusters: Thorny Flat, Dolly Sods, and the CTSI HPC Cluster. You can access them using SSH. The instructions here are valid for our main two clusters, Thorny Flat and Dolly Sods.
Regardless of which operating system you use, there is always a way to install the terminal emulator and SSH client that you need to connect to an HPC cluster. Both Linux and macOS include an SSH client by default. For these operating systems, all that you have to do is to open a terminal. On macOS, the terminal is located in Applications under the Utilities folder. On Linux, the terminal is so central that most Linux distributions create an icon directly from the desktop. Otherwise, you can search for it in your applications bar.
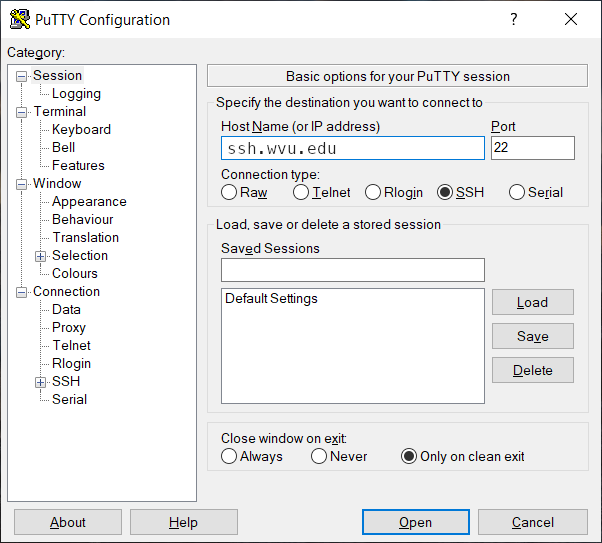
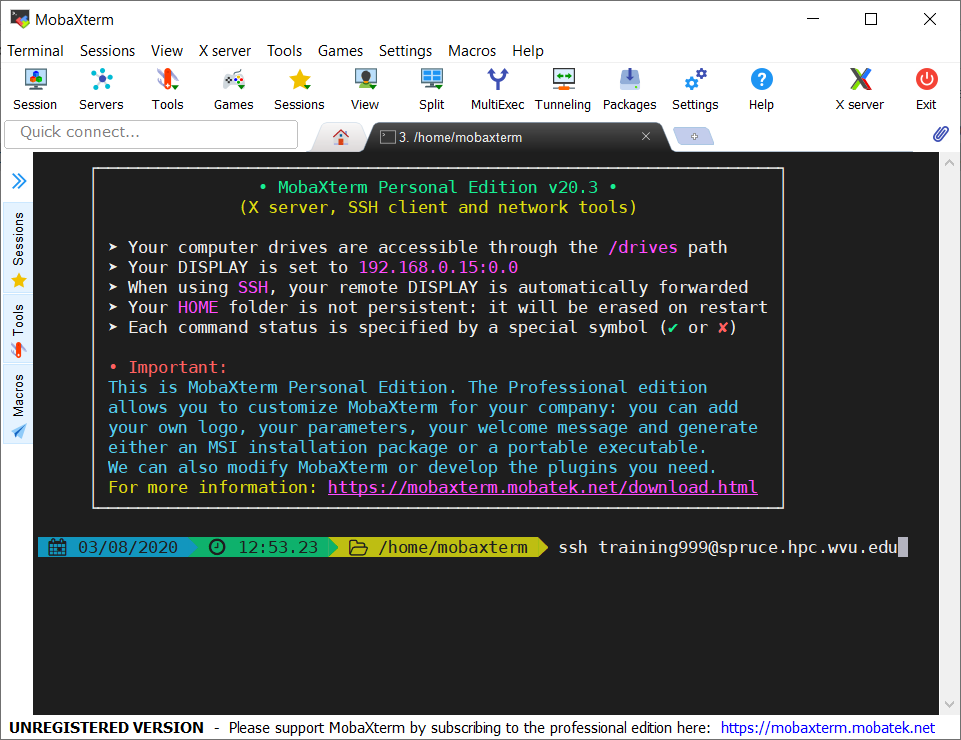
On Windows machines, you have several options. You can install an external application or use Windows utilities such as Powershell or Visual Studio Code, which are included in modern versions of Windows. For the external application, one option is a free application called PuTTY. PuTTY offers a simple SSH client that is enough for this lesson. Another option is MobaXTerm, which offers a full-featured SSH client plus the ability to open X11 windows from the remote machine. There are many alternatives to these two. As soon as the application supports the SSH protocol, you can use it to connect to the clusters.
More recently, there have also been options for accessing a terminal and SSH clients using Microsoft products. One option is to install Visual Studio Code. Instructions to add an SSH client to VSC can be found here and here. Visual Studio Code will give you remote access and a file manager that you can use to move files between the cluster and your computer.
Another alternative is using the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). WSL will allow you to run a full Linux OS inside Windows with all the commands that you will encounter on a typical Linux machine. With the latest version of WSL 2 and Windows 10 or 11, you can even run GUI applications from inside Windows alongside other Windows applications. You can see the files on your Windows machine. Running and completing Linux OS inside Windows will give you access not only to SSH client and terminal but also to the commands that you will learn during this lesson, as you will do from a Native Linux machine. Instructions about installing and configuring WSL can be found here
Connecting to Thorny Flat and Dolly Sods
Most likely, you will connect to Thorny Flat, our flagship HPC cluster. The instructions below work for our two main HPC clusters Thorny Flat which is a general-purpose HPC cluster, and Dolly Sods, which is a GPU-based HPC cluster. Accounts on those clusters are independent, so you can access one without necessarily having an account on the other.
To access Thorny Flat from your computer, execute this command from your terminal (Linux, macOS):
ssh <username>@ssh.wvu.edu
This command will allow you access to WVU’s SSH gateway. An intermediate machine that controls the access to machines inside the campus. The machine will ask for your password and DUO authentication. Once you are accepted into the system, you will see a command prompt and indication that you can start typing commands that will be executed on the SSH gateway.
The commands that will allow you to enter into the HPC clusters are: For Thorny Flat:
ssh ts.hpc.wvu.edu
For Dolly Sods:
ssh ds.hpc.wvu.edu
If you are using a GUI client such as PuTTY enter ssh.wvu.edu as the server’s name and your username in the corresponding field before connecting to the remote machine.
After entering your credentials with DUO, you get a prompt on the SSH gateway, and from there, you go to Thorny Flat.
Logging Out
Logging out of a cluster can be done with the exit command:
$ exit
Executing this command once will return you to the SSH gateway. Execute exit again, and you will leave the SSH gateway and return to a prompt on your machine.
Native terminals in various Operating Systems
There is no bash terminal default on Windows. Below are the steps to acquire one.
Enable WSL
- Press the Windows key and type "Windows Powershell".
- Right-click and "Run as administrator".
- Paste the following into the shell and press
enter.dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart- Close the Powershell and restart the computer.
Download the Ubuntu Subspace
This installation gives your Windows a little bit of Linux inside of it. Launching the Ubuntu app will give you a terminal and environment quite similar to those of a Linux machine like our HPCs. Your normal "C drive", "D drive", and so on are found under
- Press the Windows key.
- Type "Microsoft Store" and press enter.
- Search for "Ubuntu" (the search bar is in the top right of the store) and click the top-most result.
- Install Ubuntu.
/mntin the subspace. More on accessing those later.
To open a terminal:
The default terminal for MacOS, starting with Catalina is zsh. To start a bash shell, type
- Click the Launchpad icon in the Dock.
- Type Terminal in the search field.
- Click Terminal.
bashinto the terminal and pressenter.
The terminal is usually a button on your desktop. The icon is commonly depicted as a monitor with a black screen
Downloading the materials
The materials of examples and exercises can be downloaded by executing this command on the terminal.
git clone https://github.com/WVUHPC/workshops_hands-on.git
This command will download all the files used in our workshops into a folder called
workshops_hands-on. You can move into the particular folder for this workshop using the command.
cd workshops_hands-on/Introduction_HPC
If you are unfamiliar with these commands, do not worry; you are in the right class and will learn all these commands and how to use them. These and many other commands will be the topic of the material that follows.