Accessing the clusters using Secure shell (SSH)
The most common way of accessing a HPC computer cluster is via a remote shell. A remote shell allow you to execute commands on another machine same as you do sitting on front of it. A remote shell is convenient because it also allow other people to do the same, so you get access to a resource being utilized by several users at the same time.
All that you need on your computer is terminal emulator and a SSH client. A terminal emulator is a program that mimics the behavior of old dumb terminals from a few decades ago. An SSH client is a program on your computer that allow you to connect to the SSH server from another computer. In the old times (80s), people used to create a remote shell using Telnet. SSH provides a secure channel over an unsecured network such as internet. SSH offers similar capabilities to telnet but adding encryption, so all data sent and received between your computer and the remote host is encrypted in such a way that only your computer and the remote computer can see the data. If you want to know more about Secure Shell see at Wikipedia
Currently (2020) WVU has two clusters for HPC, Spruce Knob and Thorny Flat. You can access them using SSH. Both Linux and macOS include an SSH client by default. In this case all that you have to do is open a terminal. On MacOS the terminal is located at the Utilities folder inside your Applications. On Linux the terminal is so central that most linux distributions create an icon directly from the desktop.
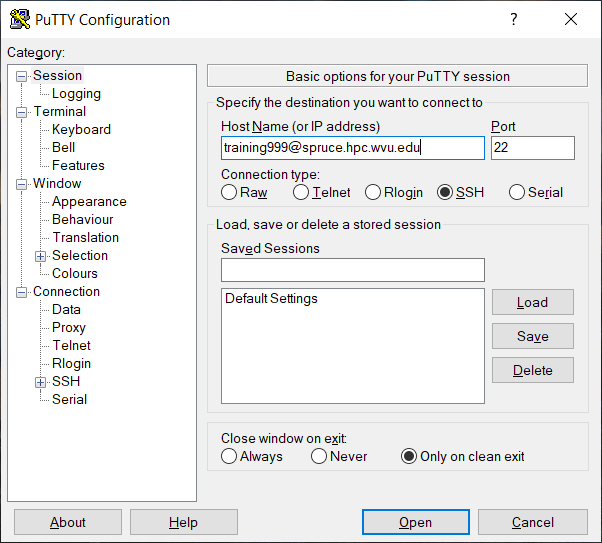
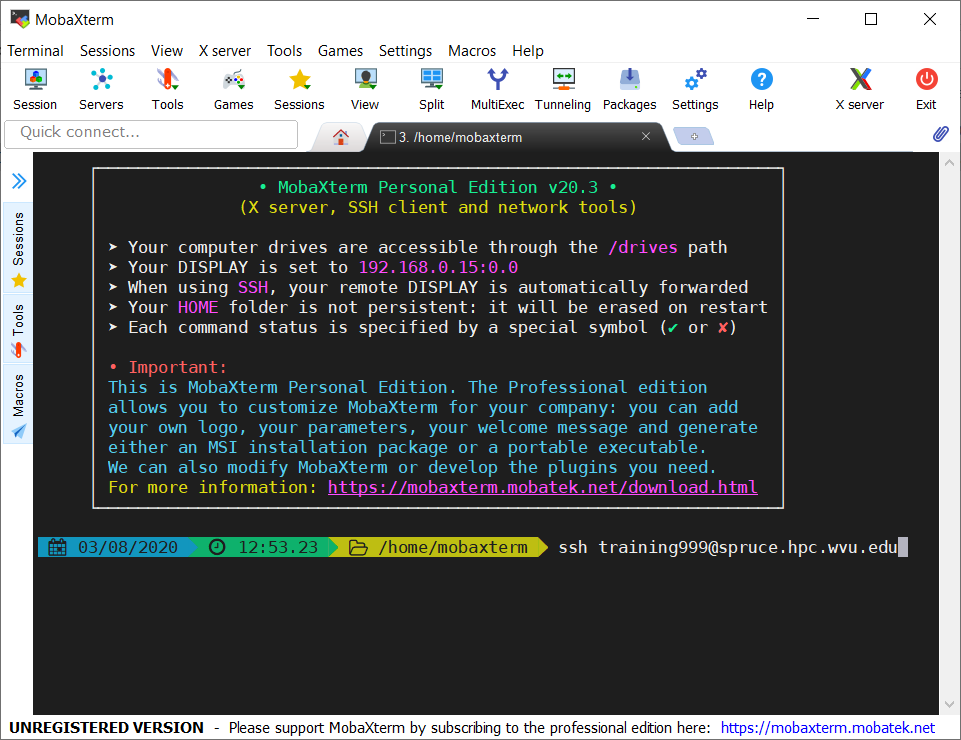
On Windows machines you need to install an external application. One option in Windows is a free application called PuTTY. PuTTY offers a simple SSH client that is enough for this lesson. Another option is MobaXTerm that offers a full featured SSH client plus the ability to open X11 windows from the remote machine.
Connecting to Spruce Knob
On your terminal execute:
ssh <username>@spruce.hpc.wvu.edu
If you received one of the training accounts, this is the machine where you will connect. For example if you username is training999, connect to Spruce using:
ssh training999@spruce.hpc.wvu.edu
After entering your credentials with DUO, you get a prompt on Spruce
Connecting to Thorny Flat
On your terminal execute:
ssh <username>@ssh.wvu.edu
Enter your DUO authentication and execute this command on the Gateway node.
ssh <username>@thorny.hpc.wvu.edu
Once you enter on the system, you can start typing commands. You can open several connections simultaneously. Each connection is independent of each other and you have to authenticate on each new terminal.
Login on Spruce
Using the username and password given to you for this training or using your own account login into Spruce or Thorny and execute the command
hostname.What do you see on the terminal?
Solution
You should get the name of the head node:
On Spruce Knob the head node is srih0001.hpc.wvu.edu
On Thorny Flat the head node is trcis001.hpc.wvu.edu
Downloading the materials
The materials of examples and exercises can be downloaded executing this command on the terminal.
git clone https://github.com/WVUHPC/Introduction-HPC_Data.git
This command will download all the files into a folder called
Introduction-HPC_Data. You can move into the directory using the command.
cd Introduction-HPC_Data
If are not familiar with these commands, do not worry, you are actually in the right class. These and many other commands will be the topic of the material that follows.