Decision trees and random forests
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 30 minQuestions
Using Scikit-learn for decision trees, decisions nad random forest
Objectives
Learn how to use Scikit-Learn to create decision trees and random forest for inductive inference
Compared with the methods previously discussed, we now focus on classifiers where the data features are not necessarily avaialable at the same time and the decisions are based on weigthing the demands of the situation. This means that we are evaluating some rules and taking decision as we go along. For this problem, we will consider the method of decision trees. A method used for regression and classification, where a set of rules are created to allow the data classification into expected outcomes.
The reliability of the information in the decision tree depends on feeding the precise internal and external information at the onset. Even a small change in input data can at times, cause large changes in the tree. Changing variables, excluding duplication information, or altering the sequence midway can lead to major changes and might possibly require redrawing the tree.
In practice, practical decision-tree learning algorithms are based on heuristic algorithms such as the greedy algorithm where locally optimal decisions are made at each node. Such algorithms cannot guarantee to return the globally optimal decision tree. This can be mitigated by training multiple trees in an ensemble learner, where the features and samples are randomly sampled with replacement (this is called Random Forest and will be discussed a bit later).
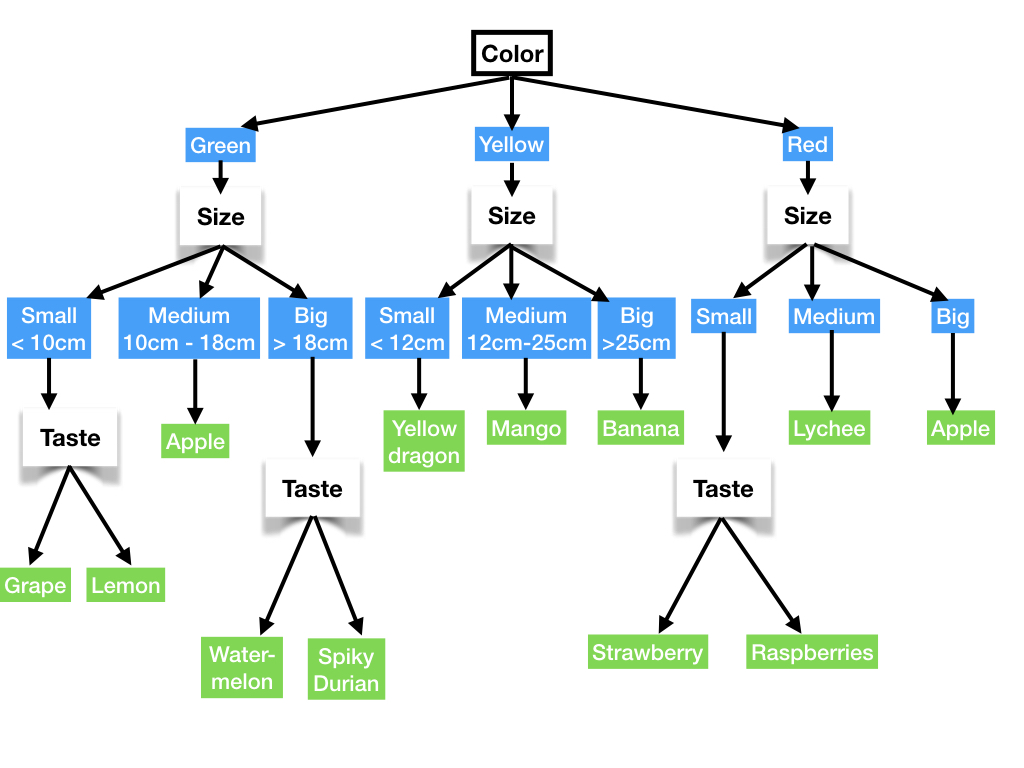
The following figure shows an example of a decision tree on how to classify some fruits based on some basic properties. In this graph, the internal nodes represent some type of attributes and the edges represent the actions. Testing each one of the nodes lead to different actions, leading to decisions over the connected edges. The process is repeated until a leaf is obtained (green boxes).
Now, it is clear that the tree shape can change depending on how the tree is built. Different methods can be used to create the tree, we will start by using the tree as a classified by using Scikit. Then, we will create our own implementation of a classifier and discuss different methods to measure the performance of the created tree.
During the course of this section, we will use the data used in section 03, therefore we advise you to go back and recreate the data reading and manipulation. We will use some of the introduced lines here without any explanation within ipython.
In [1]: import pandas
In [2]: df=pandas.read_excel("2018_all_indicators.xlsx")
In [3]: print(df['indicator_name'])
The major advantages on this methodology are:
1) Rules can be interpretated easily by the user, which makes the method very transparent.
2) Different tools can be used to visualize the decision flow chart that it is then summarized in the form of a tree, where decision options correspond to different branches and status of the classification oor outcomes correspond to different leaves.
3) The training is logarithmic with the number of points with the number of data points.
4) The data preparation is very little as in many cases te data can se used directly as it comes from the database.
5) The data can be diverse, which means that some can be numeric, some other can be a character string and some can be boolean.
6) The model can be easily assessed by simple statistical measurements.
In any case, in the use of this methodology we need to keep in mind the main disadvantages:
1) The performance of the decision tree depends quite strongly on feeding the information at the onset. This can create over-complex trees which are then very difficutl to generalize. This means that after the training, small changes in the input data can lead to large changes in the tree. Therefore, there is a high probability of overfitting the decision tree.
2) After the data is supplied, the constructed tree needs to have a predefined number of layers, the larger the number of layers the complexity also increases exponentially.
3) A decision tree with categorical variables gives a biased prediction in cases where there is a large disparity in the attributes (large difference between the number of categories).
For this section, we will make use of the same database used in the regression of section 03. Here we will assume that the database has been cured and now we can play with it directly.
virtualenv reg_hdi
The name of the virtual environment is reg_hdi. This name is arbitrary.
Now we activate the environmet with:
Key Points
Decision trees and random forest.