Introduction
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
What do we mean by Machine Learning?
Objectives
What is Machine learning. Machine learning classfication. Possible Machine learning algorithms
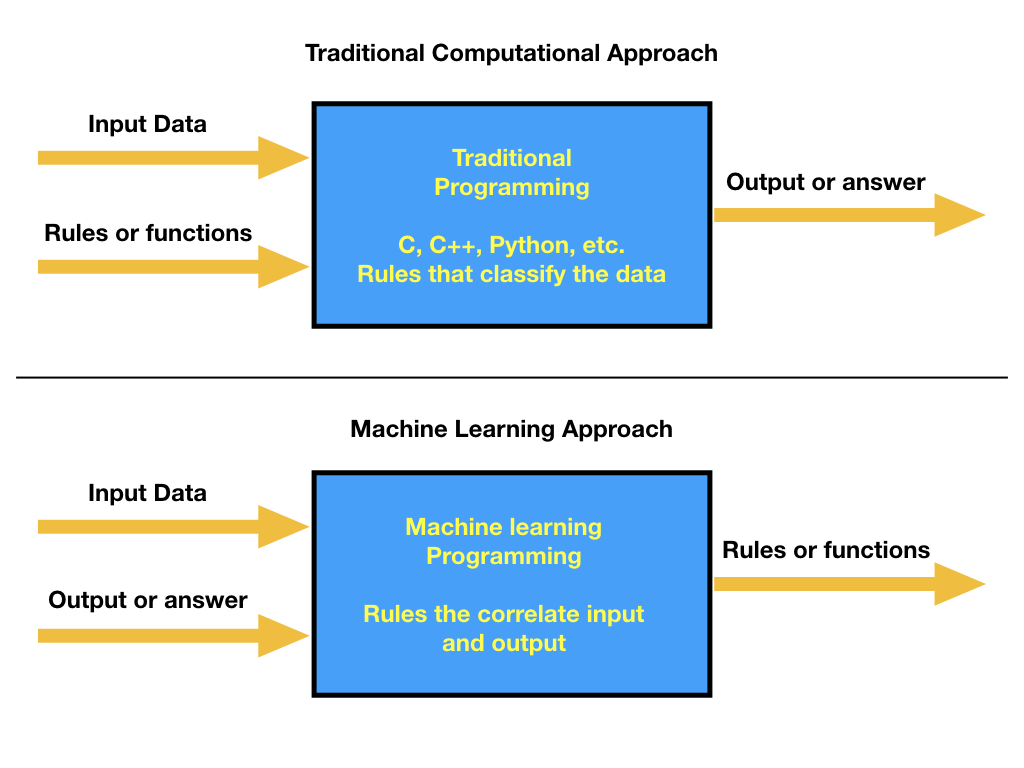
Our experience in solving a problem by using a computer always involve the idea that we have access to the data at the same time that you can define some specific rules that can be used to map an asswer. From a programming perspective, you need to create a series of rules that guarantee that given the input you get the correct output. In most cases, the input data is very diverse and the number of rules that needs to be applied to input sequences increases, making the programming scheme to fail. A different approach is based on allowing the machine to learn, which means that experience will be used to make accurate predictions. This paradigm can be view as:
In this new approach of solving problems in the computer, then our concern is to be able to create a model that will take the input and output and, by training a model, meaning allowing the computer to learn and extract the corrrelations between the provided data, we can find the model parameters that represent the rules and make a prediction (meaning that we can infer the rules in this learning process). The model parameters can be found by using past information, where the input and outpuf is completely known. Here it is important to stress that the quality and size of the available data is the key to have a very good performance of the machine learning algorithm.
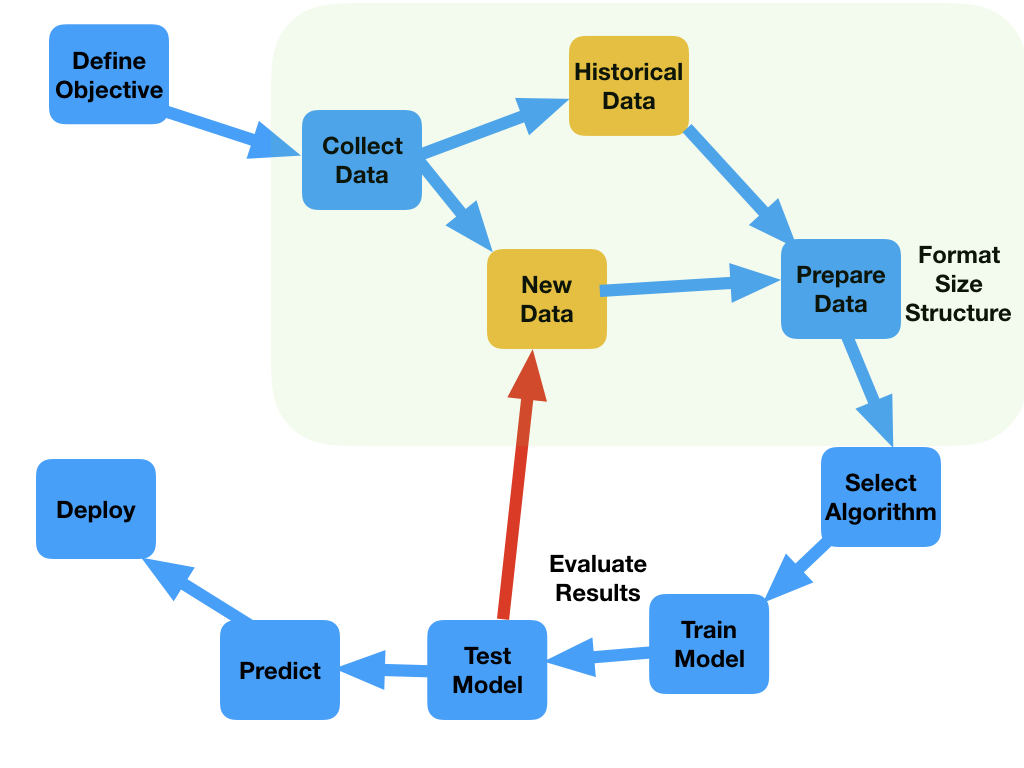
While in the classical approach, we use a computer language, we code the program with the rules that provide the right answer, we then compile the program and use it to predict an answer based on new data. This process is quie succesful when the input data is quite uniform and there is not large data variability. In the case of the machine learning, our purpose is to optimize parameters within a predefined model on data that can be quite disperse and very inhomogenenous. In reality, the methodology goes as follows:
The goal or question that machine learning will try to address needs to be defined. Based on that question, data collection is the most complicated part of any machine learning. This could happen because the data is obtained from different formats, different sources, very old databases, etc. Before the data is used, it needs to be cleaned and formatted. Even simple statistical correlations needs to be performed across different data sources. Only good quality data would give the right value to the machine learning algorithm. After the data is pruned, the machine learning model needs to be selected. There is not a clear path on that and depends on experience, practice and availability. In this tutorial, we will discuss few algorithms, but the included list here is really incomplete and we encourage the attendee to go to the WEB or to technical books to search for more methods.
The fields where this methodology have an impact are very broad and the range from voice recognition, document or music classification, material structure prediction, fraud detection, prediction of signal main components as in geophysics, matching of information as in forensic sciences, recommendation systems, etc.
Machine learning are usually categorized in supervised learning, reinforce learning and unsupervised learning. In the first case, we have access to data that can be classified and labeled previously that that can be used for training of the algorithm. With the predicted parameters, the algorithm can infer the output from a given input. One the other hand, unsupervised machine learning algorithms are useful when the available data can not be (or it is not) classified or labeled. The methodology will explore the data to infer the correlations or hidden function from the provided data. There is also the development of the so called reinforcement machine learning algorithms, which are methologies that additionally to the provided data, it can also interact with the environment. This interaction produces actions that can lead to errors or rewards that can maximize the algorithm performance. This methodology is also called active learning and it is now very fancy between practicioners.
In reality, there is a large set of learning problems and it will be really hard to include all of them in a single tutorial. That is why we have done a preselection of a broad number of possible problems:
1) Classification. Given a set of items, the algorithm should be able to classify them. The possible classification items is the one that will make the choice of the algorithm, but in general the number of possibilities needs to be small. Though there are problems as text classification or speech recognition where the number of possibilities is unbouded and still we can use classification.
2) Regression. In this problem, we are interested in predicting the outcome or a number by providing an input. This case can be unbounded as in the inputs as well as in the prediction.
3) Ranking. By providing a set of items, the algorithm should be able to order them according to some criteria.
4) Anomaly detection. Find anomalies in data based on the normal behavior. Money withdraw in bank accounts is a very good example.
5) Clustering. Creating limits between data that can define clear regions that separate them. Here we want to discover structure from unexplored data.
6) Association rule learning. Infer association pattern between the provided data.
7) Structure output. Organizing the input data in a more organized structure.
8) Dimensionality reduction. Here the algorithm reduced the dimensionality of the input into a lower dimensionality representation but keeping the most relevant properties of the initial representation.
In this tutorial, we will make use of two different open source libraries, which contain all the methods we will be describing in this tutorial but at the same time, contain more algorithms than those discussed here. Basically, we will use Sciki-Learn (https://scikit-learn.org/stable/) and TensorFlow (https://www.tensorflow.org/). We will only focuse on problems (1), (2), (4) and (5).
Key Points
Introduction to machine learning, what is the concept and why is so related to data.